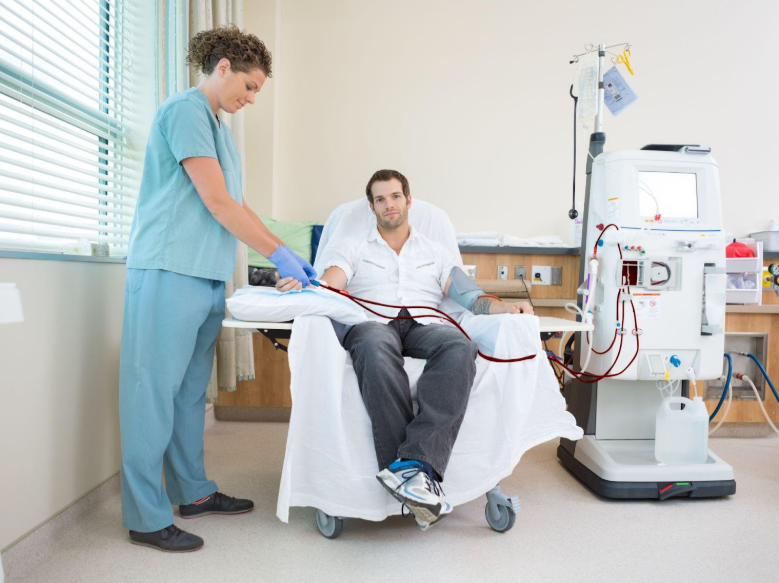
Today we would like to delve into the most frequently asked questions about dialysis. As a reminder, dialysis is a medical procedure that removes waste products, excess fluids, and toxins from the blood, as well as regulates electrolyte levels. There are two main types of dialysis: hemodialysis, which uses a machine to filter the blood, and peritoneal dialysis, which uses the lining of the abdomen as a natural filter.
What Are the Most Common Reasons for Dialysis?
Someone might require dialysis if they have any of the following conditions:
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Progression: CKD is a gradual loss of kidney function over time. As the kidneys deteriorate, they may reach a point where they can no longer adequately filter waste from the blood. Dialysis becomes necessary to perform this vital function artificially.
- End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD): This is the final stage of chronic kidney disease when the kidneys have lost almost all their ability to function.
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI): Sometimes, the kidneys can suddenly lose function due to severe infection, injury, or other causes. In such cases, dialysis may be needed temporarily until kidney function improves.
Are There Any Possible Complications Associated with Dialysis?
Some of the possible complications associated with dialysis include the following:
Infection
Both hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis involve accessing the bloodstream or peritoneal cavity, which can increase the risk of infections such as bloodstream infections (sepsis) or peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum).
Hemodialysis Complications
In hemodialysis, complications such as blood clotting and narrowing of blood vessels can occur.
Peritoneal Dialysis Complications
For peritoneal dialysis, complications may include hernias, leaks of dialysis fluid, or infections of the peritoneal cavity.
Psychological and Emotional Challenges
Coping with the demands of dialysis treatment can take a toll on a person's mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, or stress.
Do Patients with CKD and ESRD Need to Follow a Special Diet?
While the diet may differ based on individual circumstances, there are some general guidelines to keep in mind:
Limit Protein
Reducing protein intake can help lessen the strain on the kidneys, as protein metabolism produces waste products that the kidneys must filter. However, it's best to ensure an adequate intake of high-quality protein to prevent malnutrition. A dietitian can help determine the appropriate amount of protein for each individual.
Limit Phosphorus
High levels of phosphorus in the blood can weaken bones and lead to cardiovascular complications. Foods rich in phosphorus, such as dairy products, nuts, and certain types of meat, may need to be limited, and phosphorus binders may be prescribed to reduce absorption from the diet.
Control Sodium (Salt) Intake
Too much sodium can lead to fluid retention and high blood pressure, both of which can worsen kidney function. Limiting sodium intake by avoiding processed foods, canned goods, and salty snacks can help manage blood pressure and fluid balance.
Manage Fluid Intake
For individuals with CKD and ESRD, fluid intake may need to be restricted to prevent fluid overload and swelling. Monitoring fluid intake, including beverages and foods with high water content, can help maintain a healthy fluid balance.
Consider Calorie Needs
Depending on the stage of kidney disease and individual factors, calorie needs may vary. It's important to ensure adequate calorie intake to prevent malnutrition and maintain energy levels.
Work with a Dietitian
A registered dietitian who specializes in kidney disease can provide personalized dietary recommendations based on individual needs, lab results, and medical history.
Can Patients with CKD and ESRD Travel?
Here are some tips for patients with CKD and ESRD who wish to travel:
- Arrange Dialysis Treatment: It is important to contact a dialysis center at the destination far in advance to schedule appointments and ensure availability during the travel period. Some patients may opt for home dialysis equipment or portable dialysis devices for greater flexibility.
- Plan Medications and Prescriptions: It is important for patients to ensure an adequate supply of medications and prescriptions for the duration of the trip, including any medications related to kidney disease management, blood pressure control, or other underlying conditions. We recommend carrying medications in their original packaging and bringing a list of medications and dosages.
- Emergency Preparedness: We advise carrying a medical alert card or bracelet indicating kidney disease and emergency contact information.
What Are the Support Options Available for Patients with CKD and ESRD?
Depending on the individual's needs and financial resources, there are several options available:
Counseling and Mental Health Support
Counseling services and mental health professionals can provide emotional support, coping strategies, and tools to address stress, anxiety, depression, and other psychological challenges associated with kidney disease.
Support Groups
Joining support groups for kidney disease patients can provide emotional support and valuable insights into living with CKD and ESRD. Support groups may meet in person or online, allowing patients to connect with others facing similar challenges, share experiences, and exchange practical tips for managing their condition.
Patient Education Programs
Many healthcare facilities, including those at Metairie Kidney Center, offer
patient education resources specifically designed for individuals with CKD and ESRD. Various education programs cover topics such as kidney disease management, dialysis procedures, dietary guidelines, medication management, and coping strategies. Education programs empower patients with the knowledge and skills to actively participate in their care.
At
Metropolitan Kidney Center, our nurse-to-patient ratio of 4 to 1 allows us to provide individualized patient care. Feel free to
contact us or
schedule a visit with us to learn more about our approach and services.